|
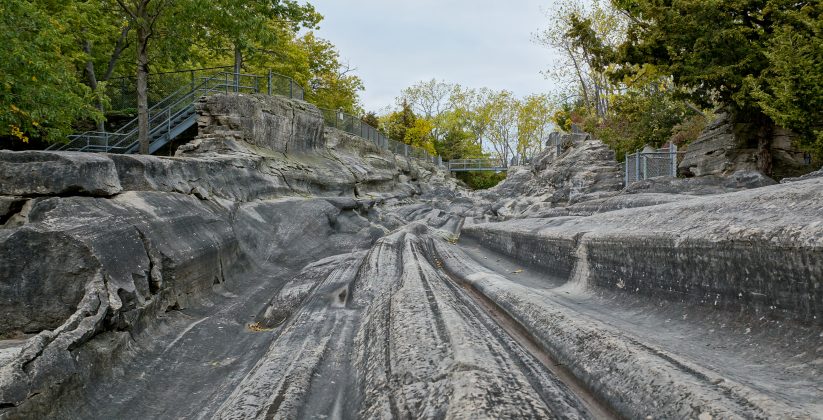
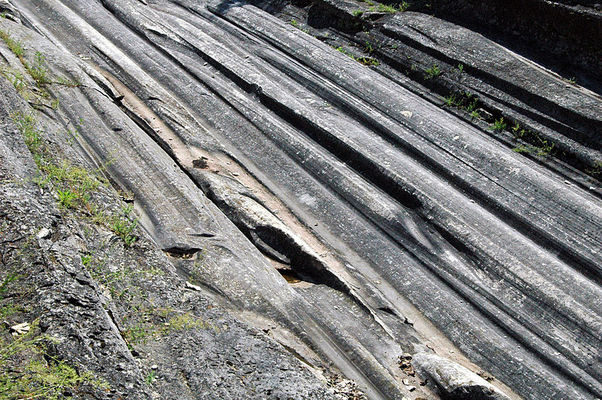
Glaciers to Great Lake: Ohio would not be what it is today without the impact of glaciers during the Ice Age. Glaciers left behind more than just till deposits in Ohio, glaciers also helped make Lake Erie. Check out this video and learn more about Ohio's Ice Age: http://www.pbs.org/video/wptd-our-ohio-glaciers-great-lake/ (Running time: Approx. 2 minutes) - WCET Cincinnati, Our Ohio series Glacial Grooves State Park, Kelley's Island These glacial grooves were carved out during the Pleistocene Epoch (the last Ice Age). Stories in the Stones Underneath the soils of Ohio lies a vast record of history embedded in rocks and minerals: http://geosurvey.ohiodnr.gov/news-events/multimedia-library Etched section of hand sample of Columbus Limestone from quarry on Kelley's Island. The circular feature is a crinoid columnal. Glacial Map of Ohio: geosurvey.ohiodnr.gov/portals/geosurvey/PDFs/Glacial/glacial.pdf Flint is Ohio's official gemstone. Flint Ridge Flint is renowned for its color and beauty. In pre-historic times, flint was used by American Indians for tools, including knives and spear points. The flint polished stone is valued in jewelry making today. Licking and Western Muskingum Counties are known for having the most famous deposit of flint in Ohio; this area is better known as Flint Ridge. Flint Ridge Flint became Ohio's official gemstone in 1965.
Ohio's Geological Walk Through Time Located at the Natural Resources Park on the Ohio State Fairgrounds, this exhibit offers a unique learning experience for anyone interested in Ohio's natural history, including fossils, rocks & minerals, and more. www2.ohiodnr.gov/ohio-state-fair/geological-walk
Geoscience News and Information - more on rocks, minerals...geology.com/ Learning about rocks and minerals gives a deeper appreciation of the story behind the scenery in our National Parks. - National Park Service Yellowstone National parkRocks and minerals are all around us and used in our everyday lives. They also help us to develop new technologies. Rocks and minerals are used in building material, cars, roads, appliances and even in cosmetics. Humans need to consume minerals on a daily basis in order to maintain a healthy lifestyle that includes strengthening the body. Abiotic features, like rocks and minerals, play a valuable role in our natural systems such as providing soil nutrients in Redwood where the tallest trees in the world grow or provide habitat like the cliffs at Grand Canyon National Park where endangered condors nest. We can learn more about Earth's materials, structure, and systems through studying rocks and minerals. "Natural objects, such as rocks and minerals, contribute to the beauty and wonderment of the National Parks and should be left, as they were found, so that others can experience a sense of discovery." - https://www.nps.gov/subjects/geology/rocks-and-minerals.htm Glacier National Park, MTWaterton - Glacier International Peace Park World Heritage Site Glacier's pristine forests, alpine meadows, rugged mountains, spectacular lakes and wildlife are truly spectacular sites. dEATH vALLEY nATIONAL pARK, ca, nvHottest, Driest, and Lowest National Park: Steady drought and record summer heat make Death Valley a land of extremes in this "below-sea-level basin". Each "extreme has a striking contrast": towering peaks are frosted with winter snow, rare rainstorms bring vast fields of wildflowers, lush oases harbor tiny fish along with refuge for wildlife and humans. "Despite its morbid name, a great diversity of life survives in Death Valley."
Educators and Volunteers - "Natural Parks are America's Largest Classrooms!" https://www.nps.gov/teachers/index.htm Science in your National Parks: https://www.nps.gov/nature/index.htm
0 Comments
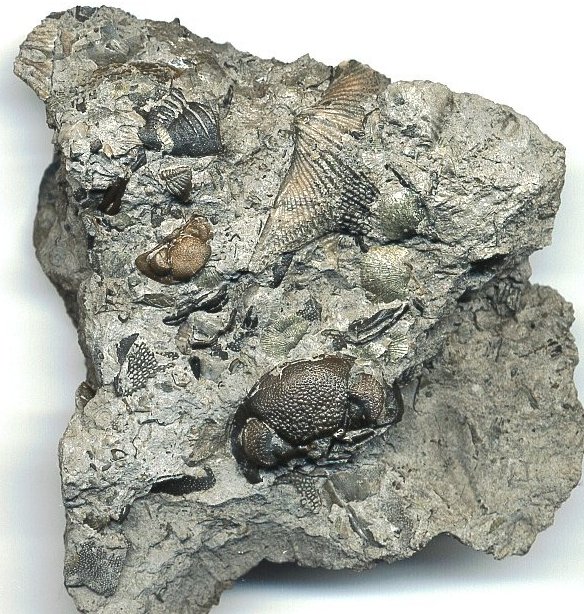
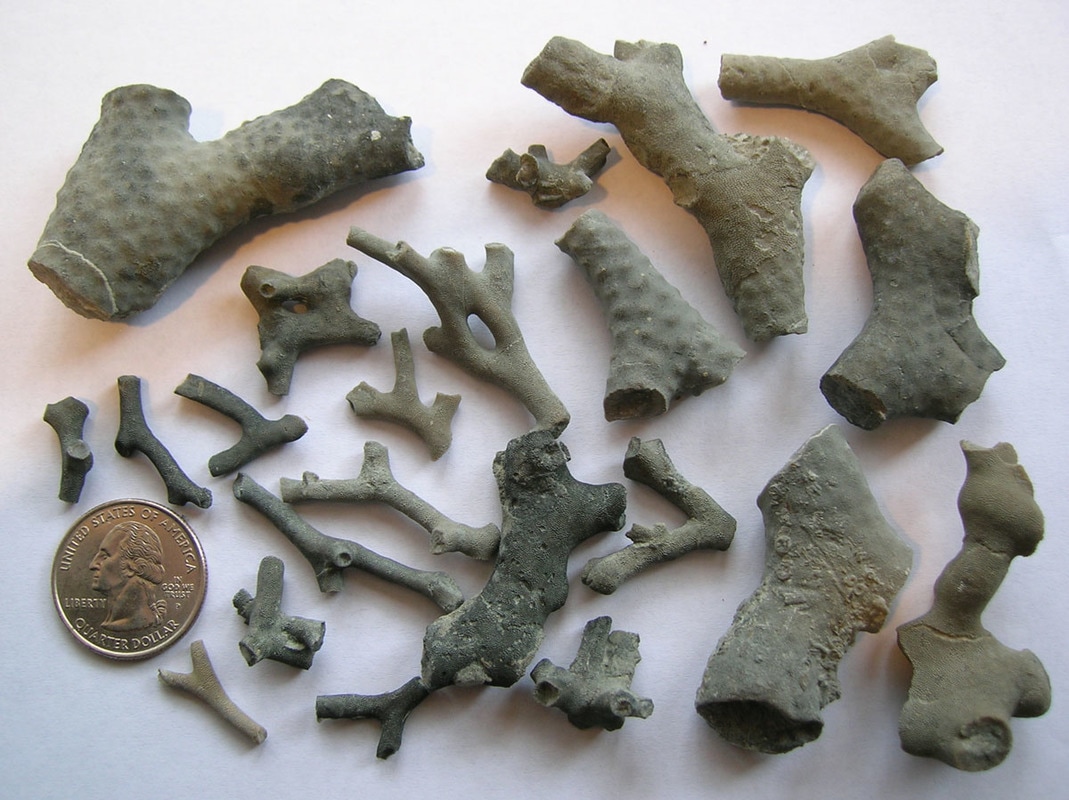
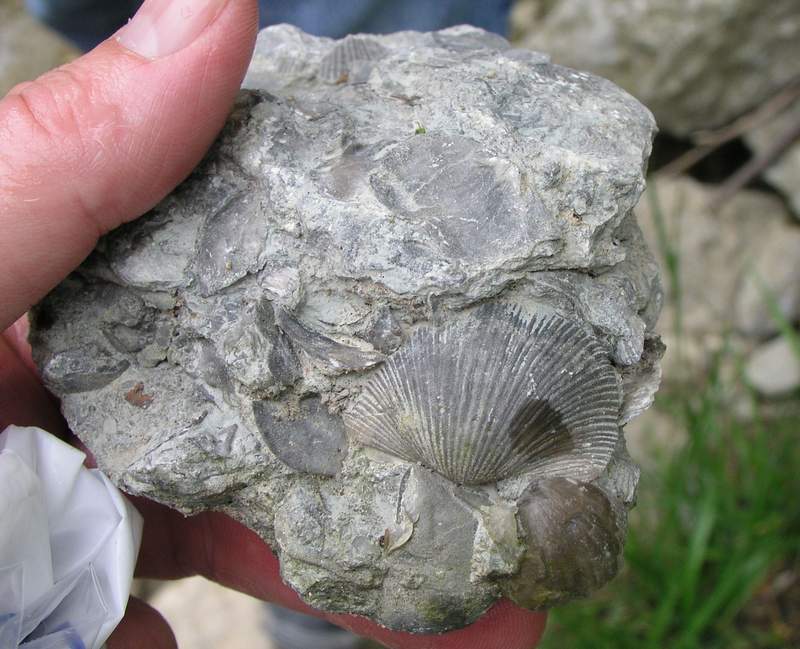
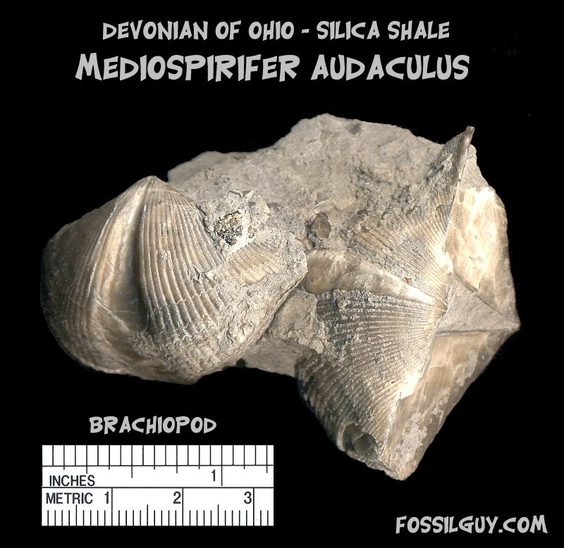
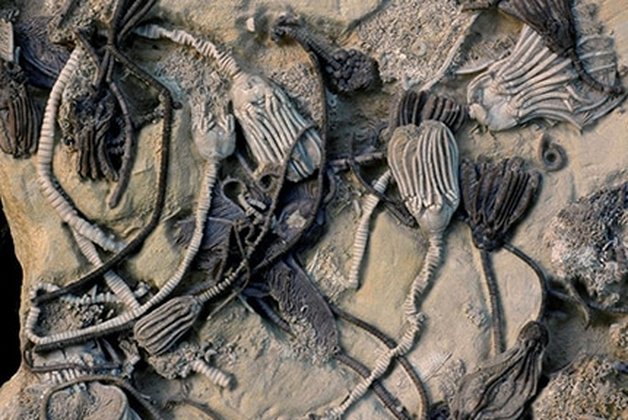
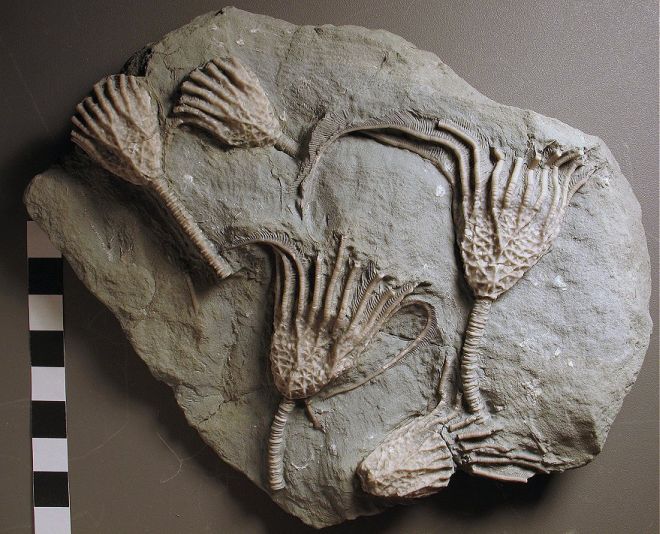
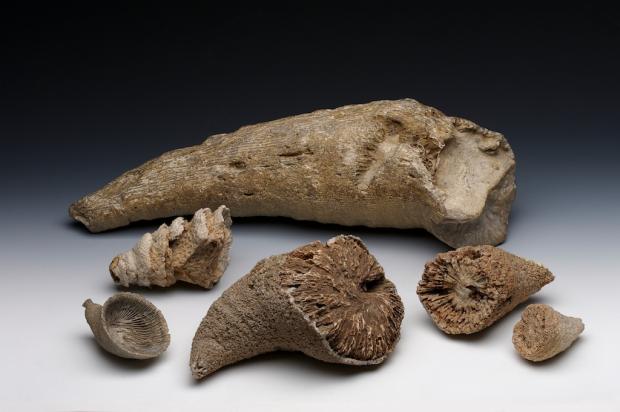
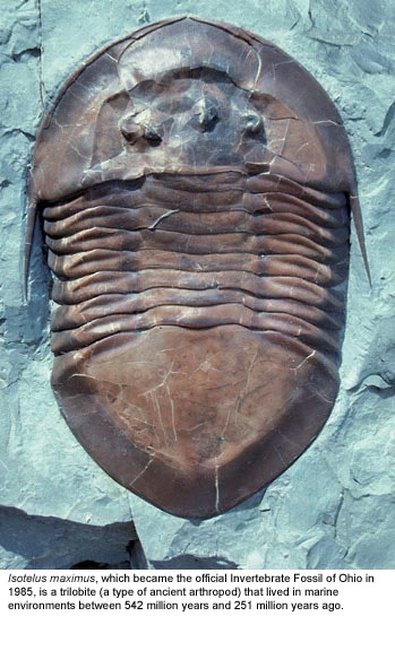
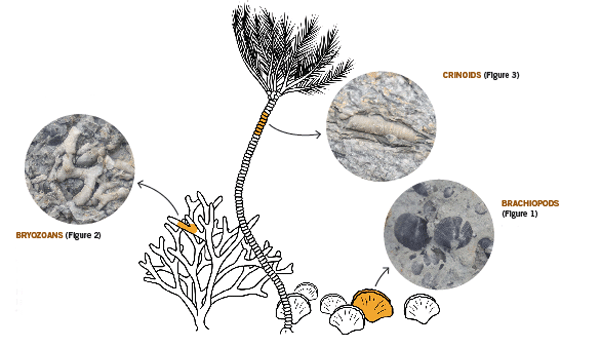
What is a Fossil? A fossil is the naturally preserved remains or traces of organisms that lived in the geologic past. There are two main types of fossils; body and trace. Body fossils include the remains of organisms that were once living and trace fossils are the signs that organisms were present (i.e. footprints, tracks, trails, and burrows). - imnh.isu.edu/digitalatlas/geo/basics/fossil.htm "Any direct evidence of ancient life, including the remains or traces of plants or animals. The term "fossil" does not include any life forms that have been buried since the beginning of historic time." - www.ohiohistorycentral.org/w/Fossil  Ohio's Geologic Timeline: "Since the oldest sedimentary rocks in Ohio were deposited first, they lie below the youngest rocks. Therefore, if a layer of sedimentary rock lies on top of another layer of such rock, the top layer is younger than that beneath it. This holds true in Ohio EXCEPT in cases where a force has disturbed the layers after they were deposited." - www.ohiohistorycentral.org/w/Ohio%27s_Geologic_Timeline  Fossils of Ohio – A great tool to help identify fossils found throughout Ohio, designed for use by beginners to professionals geosurvey.ohiodnr.gov/major-topics/fossils-in-ohio Most land in Ohio is private property. Always obtain permission before collecting fossils. Most public lands (local, state, or federal) do not permit fossil collecting, except in designated areas. Fossils and Fossil Hunting in Ohio Once covered by vast tropical seas and later by giant glaciers, Ohio's landscape features an abundance of fossils. The glaciated portions of Ohio are home to Ice Age fossils, including plants and ancient mammals. But southwestern and northwestern Ohio boast a wider variety of much older marine fossils, including the official state fossil Isotelus maximus. In fact, the greater Cincinnati region lures paleontologists, fossil collectors, and rock hounds from all across the country and beyond who seek and have discovered some of the best fossil specimens in the world. - geosurvey.ohiodnr.gov/major-topics/fossils-in-ohio Public Sites in Southwest Ohio - Visitors should contact park management staff prior to collecting to obtain any permits and/or rules that may apply. Caesar Creek State Park (Clinton/Warren Counties) – Geology: Ordovician; fossils ranging from 450 to 500 million years old found in limestone forming the crest of the Cincinnati Arch. Collecting rules apply and a permit must be obtained at the U.S. Army Corps of Engineer's Visitor Center, which also features a display of fossils found at the park. For more information about fossil hunting at Caesar Creek, call (513) 897-1050. Cowan Lake State Park (Clinton County) – Geology: Ordovician; fossils ranging from 450 to 500 million years old found in limestone forming the eastern edge of the Cincinnati Arch. Special permission to collect fossils must be obtained from Ohio State Parks. For more information, call (513) 897-3055. East Fork State Park (Clermont County) – Geology: Ordovician; fossils ranging from 450 to 500 million years old in interbedded shale and limestone. Collecting rules apply. A permit must be obtained at the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Visitor Center. For more information, call (513) 734-4323. Hueston Woods State Park (Preble/Butler Counties) – Geology: Ordovician; fossils ranging from 450 to 500 million years old in limestone and dolomite forming the western edge of the Cincinnati Arch. For more information, call (513) 523-6347. Oakes Quarry Park (Greene County) – Geology: Silurian; fossils around 425 million years old. Located in city of Fairborn, northeast of Dayton. For more information, call (937) 754-3090 or see ( Ohio Geology, 2008 No. 2[800 KB PDF]. Stonelick State Park (Clermont County) – Geology: Ordovician; fossils ranging from 450 to 500 million years old in interbedded shale and limestone. For more information, call (513) 734-4323. Trammel Fossil Park (Hamilton County) – Geology: Ordovician; fossils ranging from 450 to 500 million years old in interbedded shale and limestone. For more information, call (513) 563-2985. drydredgers.org/caesar_creek.htm www.fossilguy.com/sites/caesar-creek/caesar-creek-fossils.htm#trilobite What are the oldest fossils? The earliest evidence of life on earth is of marine animals, during the Precambrian era. But there is only sparse evidence of life before the Cambrian era. The oldest known Precambrian rocks, found in Africa and Australia, are believed to be more than three billion years old. The fossils found among them are of the oldest known organisms on earth. Usually, fossils found in these old rocks are microfossils, such as elongated bacteria, Eobacterium and other water environment fossils. Bacteria represents the first stage of recognizable organized life and scientists have found well defined remains of algae and bacteria from nearly two billion years ago. Where are most fossils found? The most common fossils are found in sedimentary rock. Sedimentary layers act as evidence of the changing climate or movement of the continents during the passage of time. The Law of Superposition or Steno's law states that in a pile of undisturbed sedimentary rock, the oldest bed will lie at the bottom and the youngest on top. Layers of strata in different locations may have the same composition but carry fossils of a different time period, therefore a technique of zoning or an index fossil is used. Index fossils are specific animals or plants that had a broad geographical distribution but existed for relatively short periods of time. These fossils allow geologists to establish a parallel between layers of sediment. Some excellent guide fossils are ammonites; each species lived for relatively short periods of time but had such a broad geographical distribution. They can be found today in stratigraphic rock layers often separated by great distances. The appearance of the same ammonite in different layers in different localities gives evidence that those layers were deposited at the same time. Each time period is marked by an abundant radiation of many new life forms or the mass extinction of past life forms. - www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/paleo/fossils/index.html "Many world-famous paleontologists—geologists who study fossils—began their careers as youngsters collecting fossils in their native Ohio. Fossils from Ohio are important constituents of museum collections throughout the United States and Europe." - Fossils Collecting in Ohio ODNR GeoFacts - geosurvey.ohiodnr.gov/portals/geosurvey/PDFs/GeoFacts/geof17.pdf As previously conveyed, "Fossils" are the remains of an ancient organism or the traces of activity of such an organism. There are two types of fossils: body fossils and trace fossils. Body fossils include preserved remains of an organism (i.e. freezing, drying, petrification, permineralization, bacteria and algea). Trace fossils are the indirect signs of life that give evidence of the organism's presence (i.e. footprints, burrows, trails & other evidence of life processes). www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/paleo/fossils/index.html What are cast and mold fossils? Casts and molds are types of fossilization where the physical characteristics of organisms are impressed onto rocks, especially coarse porous rocks such as sandstones. Typically, the hard parts of an organism ( shells of mollusks, skeletal structures of coelenterates, bones and teeth of vertebrate, chitinous exoskeleton of arthropods, trunks of trees, and many sphenophyte ) leave the best impressions. These hard structures are usually composed of calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate, silica, or chitin, and do not decay as easily. The rigidity of the hard body parts also allows the sediment to form around the organism. Soft body parts decay too fast for impressions to form and are not rigid enough for a mold to set around. Fossilization Process: The fossilization process begins when the whole organism or hard body part is trapped in sediments. Because most of these body parts are typically composed of substances which are soluble in carbonated water, this entrapment usually occurs in coarse and porous rock such as sandstones. The porous nature of the rock enables the carbonated ground water to permeate and dissolve the original tissue leaving a detailed mold of the organism. Two types of molds result from this process: external and internal. An external mold is created with the dissolution of the organic which then leaves an empty cavity imprinted with the external details of the organism. An internal mold may form with hollow structures. The "shell" of the organism is filled with various inorganic materials such as sediment or crystals. When the shell dissolves, it leaves an impression of the interior surface of the shells (e.g., muscle scars) on the material. A cast of the organism can then be made using the two types of molds. Natural casts are formed when minerals are deposited within the mold. Casts can also be synthetically created when the molds are filled or covered with synthetic material, such as latex or plaster of paris, to generate a replica of the organism. In this manner, cast and mold fossilization enables us to "recreate" the structure of the organism. However in the creation of the cast, some details of the skeletal structures are lost. www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/paleo/fossils/casmol.html BRACHIOPODS (Figure 1) “Lampshells” are sea animals with hard shells that were hinged at the rear. The Flood ripped the shells apart, burying piles of them in slabs of limestone. BRYOZOANS (Figure 2) “Lace corals” were colonies of sea animals that lived together in connected modules, called zooids. The Flood tore apart these colonies, leaving only piles of broken “stems” and “branches.” CRINOIDS (Figure 3) “Sea lilies” were animals that attached to the seafloor on long columns. The Flood tore apart their bodies, leaving only piles of broken pieces of the stems, called “columnals.” https://answersingenesis.org/fossils/fossil-record/cincinnati-built-on-a-fossil-graveyard/ Types of Fossils: Fossils undergo a variety of different fossilization processes, depending on the characteristics of the particular organism. There are various levels of fossil preservation, each containing its own clues pertaining to the organism. Fossilization at the cellular level varies in all organic compounds since not all cellular types are equally resistant to decay and decomposition. The same hold at the tissue level, where some tissue types are more susceptible to fossilization. The other two kinds include the organ level and organism level which provide information in the field of morphology and biology of the ancient organism. Although there are an endless number of categories, we will focus on the broader mode of classification. Permineralization: is the occurrence of decay of organic substances and filling of mineral material into every cavity of the organism, still retaining most information about the fossil.
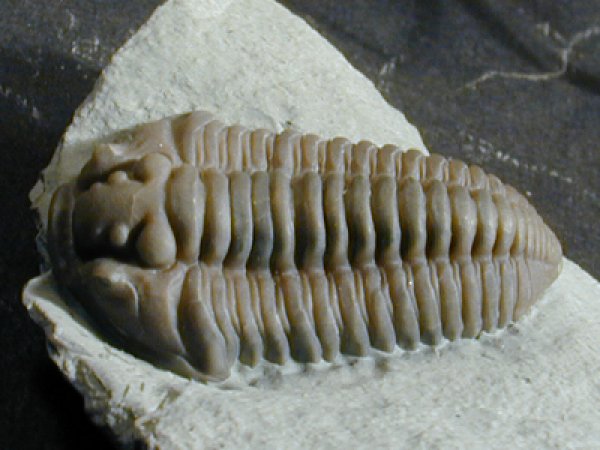
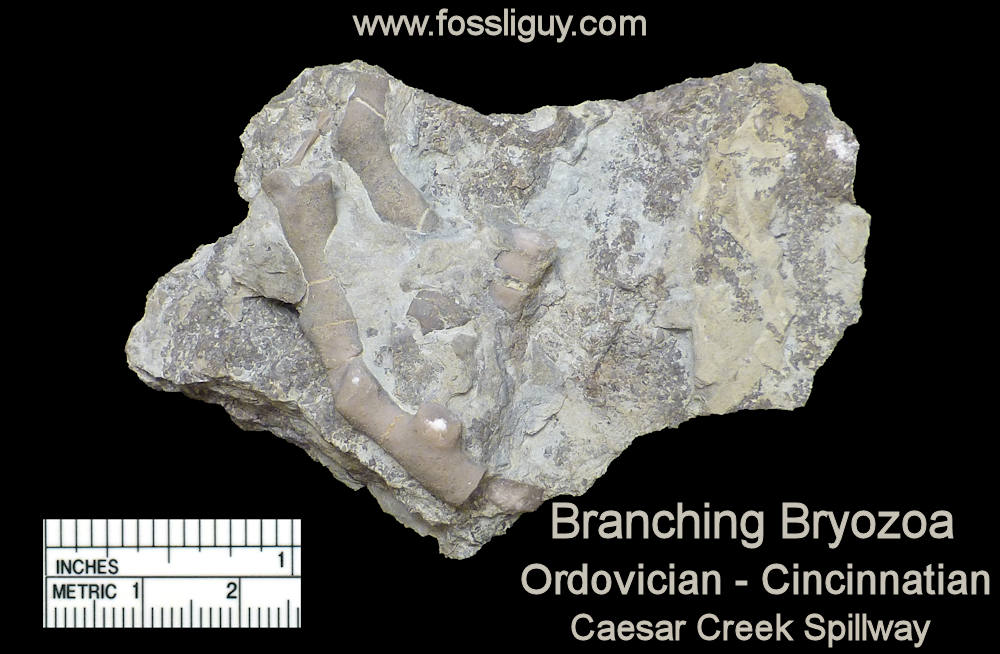
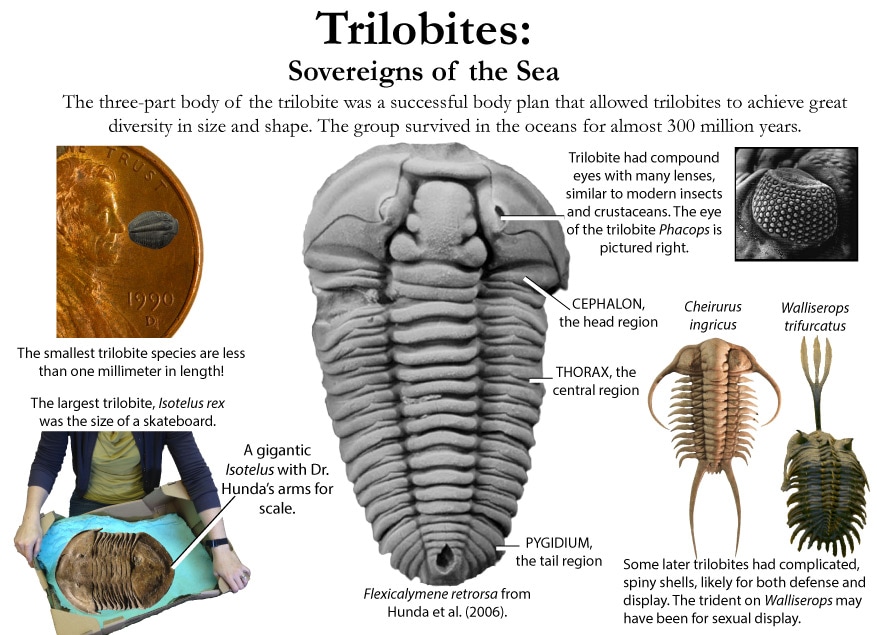
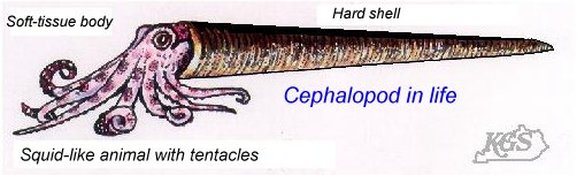
Additional Links: Visit one of these websites to learn and research more about Ohio's Fossils. This can assist you in identifying your own fossils. Schedule a trip to fossil hunt or tour a museum to explore fascinating exhibits and examine rocks, minerals, and fossils from Ohio and around the world....plus much more. DRY DREDGERS – A CINCINNATI-BASED ASSOCIATION OF AMATEUR GEOLOGISTS AND FOSSIL COLLECTORS CLEVELAND MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY & SCIENCE – AT CINCINNATI MUSEUM CENTER ORTON GEOLOGICAL MUSEUM – AT THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF EARTH SCIENCES Ohio's Geological Walk Through Time Located at the Natural Resources Park on the Ohio State Fairgrounds, this exhibit offers a unique learning experience for anyone interested in Ohio's natural history, including fossils, rocks & minerals, and more. www2.ohiodnr.gov/ohio-state-fair/geological-walk University of Cincinnati Department of Geology Covered in Shells (Greater Cincinnati): thenaturalhistorian.com/2011/09/14/covered-in-shells-how-many-fossils-are-there/ Smithsonian Natural Museum of Natural History - The Department of Paleobiology: http://paleobiology.si.edu/index.html Virtual Museum of Geology: www.virtualmuseumofgeology.com/ Other State Geological Survey Web Sites (via AASG) Geology Departments at Ohio Colleges and Universities Ohio Rock and Mineral Clubs—Listing from the Midwest Federation of Mineralogical & Geological Societies. Geology and Science Education Web Sites Science Education Associations AGI Classroom Activities for K-12 Students How are fossils found? There are certain techniques that paleontologists might exercise to find fossils, but it mostly has to do with chance and luck. However, all paleontologists need a place to start. Paleontologists must have an extensive knowledge of the stromatolites, the different eras, and which environment was most suitable for certain organisms. With this information, a collector can eliminate certain localities in his or her search. For example, if a collector was interested in finding fossils of animals of ancient rocky shores, he or she would eliminate formations and beds in which remains are likely to be rare and poor. Paleontologists can also follow leads that other paleontologists or collectors have left behind in published reports. These clues help narrow the focus of the search. For example, marsh plants are most abundant in shales and sandstones between beds of coal, and coals are found in limy shales and massive limestones, many of which are the remains of ancient reefs. Using these techniques, the process of elimination, and perhaps some luck, paleontologists have retrieved many different fossils and animal remains from a variety of geological areas. Conditions that lead to fossilization: There are many conditions that contribute to the formation of fossils. The most common include the possession of hard parts, such as a skeleton or shell, and a rapid burial after death. Besides being tough and hard, the organism must come to rest in a place where it can be buried before it decays or disintegrates. If the organism is not buried deeply and quickly, aerobic bacteria will reduce it to rubble. Water, given enough time, can also dissolve it. For this reason, fossils of some organisms are more rare than others. The skeletons that contain a high percentage of mineral matter are most readily preserved. The soft tissue that is not intimately connected with skeletal parts is least likely to be preserved. Other conditions that lead to fossilization include resting an environment that was biologically inert, areas that are receiving a large, steady supply of sediment (deltas of major rivers), and parts of the earth below sea level compared to those above the sea level. The ideal place to become a fossil is at the bottom of a quiet sea or lake where the prospective fossil is safe from damage and can be covered rapidly with sediment. Clay offers excellent conditions where the sediment protects the tissues and helps to exclude predators and solvent water. - www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/paleo/fossils/index.html Trammel Fossil Park - "A Rocking Good Time" http://www.familyfriendlycincinnati.com/2011/05/24/trammel-fossil-park-a-rocking-good-time/ "The Corryville Formation is named after the Corryville neighborhood of Cincinnati, near the University of Cincinnati. Fine particles settling out of the seas formed the shale layers that you see in the Corryville. These fine particles resulted from erosion and runoff from the uplifted Appalachian Mountains, east of this region. From the Corryville shale, some of the most rate fossils have been found. In many other local areas, the soft shale has eroded away. Trammel Park is unique in that the Corryville Formation is exposed and undisturbed."- http://local.aaca.org/siraaca/Fossils.htm What do fossils tell us? "Different fossils, depending upon how they were preserved, tell us different things. For example, fossils that are preserved in amber give us an extraordinary amount of information about the anatomy of that organism; since the organisms that are preserved in amber, mostly insects, are usually preserved intact without any disintegration of organs, muscles, and coloring. Even bones may tell a great deal about the soft anatomy. For instance, the area where the muscle attaches to the bone leaves marks that indicate size, shape, and functions of these varied organs. Also, the cavities and the the channels in skulls give us an idea of their intelligence, behavior, and their principle features. Certain parts of certain fossils can also tell us about growth, injury, disease, form, function, activities, and instincts. Fossils also record the successive evolutionary diversification of living things, the successive colonization of habitats, and the development of increasingly complex organic communities. Fossils can tell a great deal about their surroundings and the conditions under which they lived. Finally, study of fossils contributes greatly to the study of evolution. They are the only direct record of what has occurred in sequences of reproducing populations and in the course of the time on an evolutionary scale." www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/paleo/fossils/index.html Trilobite Fossils: Trilobites are a group of extinct arthropods (similar to crustaceans) with a hard shell. They are common in Ordovician rocks in the Cincinnati Arch. Unfortunately, almost all are fragments. Occasionally whole ones are found. The whole trilobites are usually found enrolled. There are over a dozen trilobites found in this strata. The most common two are Flexicalymene and Isotelus. www.fossilguy.com/sites/caesar-creek/caesar-creek-fossils.htm#trilobite "This is a typical flexicalymene retrorsa minuens trilobite fossil that can be found at Caesar Creek. Flexicalymene trilobites in the Caesar Creek area are reduced in size and most often found enrolled. They are usually the size of a fingernail or smaller. When searching for them, they superficially look like tiny brachiopods, so take your time, look closely, and you may find one!" Bryozoans are tiny colonial organisms, often mistaken for corals. The individual bryozoan is usually less than 1 mm in size. Bryozoan colonies can be branching, twiglike, fan-like, or encrusting. The entire colony is referred to as a zoarium. Some bryozoan colonies are smooth and others have monticules or bumps covering them. Each small opening or aperture was the home for an individual bryozoan or zooecium. The small animal seals the hole with a “door” or vestibule. They are difficult to identify without microscopic study. Sometimes the pattern of the apertures, size, or shape is characteristic and can be used for generic identification. Brachiopods are marine animals that have a shell made of two valves, which usually differ in shape and size. Brachiopods are closely related to the bryozoans. Brachiopod comes from Latin and means "arm" + "foot" and bryzoan means "moss animal" Brachiopods are solitary marine organisms that live between two valves or “shells.” They are very common in the Cincinnatian rocks of Ohio. They are externally different from the pelecypods (clams) in that the left and right halves of the brachiopod shells are usually mirror images of each other (see picture below). Internally, brachiopods are completely different from the pelecypods. Brachiopods feed with a special filtering organ called the lophophore which is located between the valves and attached to the brachial valve. The pedicle extends through a small opening or hole in the pedicle valve and is used as an anchoring device. The interior of the brachial valve is important in taxonomic differences between various species. Crinoids Crinoids are echinoderms that live on a long stalk, or column. Their crown is similar to an upside down starfish. Cross sections of the column usually have a tiny star within them. Columns and columnals are the most common parts found, although occasionally a crown or calyx can be found. It is rare to find the entire crinoid preserved. Crinoids are classified taxonomically by the characteristics of their crown, which makes identification of individual columns and columnals difficult unless the crown is attached. Crinoids are a sort of sea lily, an animal which attaches itself to the ocean floor, has a columnar stem and a flowery type of head. Crinoid comes from a Latin phrase that means "like a lily" Gastropods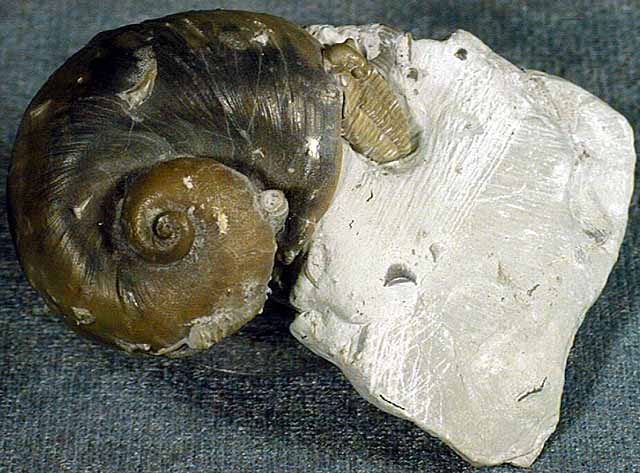  The gastropods, or snails, are extremely diverse inhabiting marine, fresh water and terrestrial environments. Their shell can coil in a conical (conispiral) or in in single plane (planispiral). Cephalopods are members of the phylum Mollusca and include squid, octopi and the pearly nautilus. Cincinnatian cephalopods were straight shelled squids. The siphuncle connects the cameras (chambers) together. The squid could pass air to the chambers via the siphuncle to make it float higher in the water or sink as it swam. Horn Corals Phylum Cnidaria contains the corals, jellyfish, and anemones. Corals can be solitary or colonial. Corals have a rich fossil record because they excreted a hard calcium carbonate exoskeleton that preserves well. The Cincinnatian solitary corals are quite large, and are “horn” or “tooth” shaped. Individuals in the colonial corals are usually quite small, coralites being 1-3 mm in diameter. Additional References: Fossils of preserved remains can be:
Trace fossils are evidence left of past animal behavior. Some examples include:
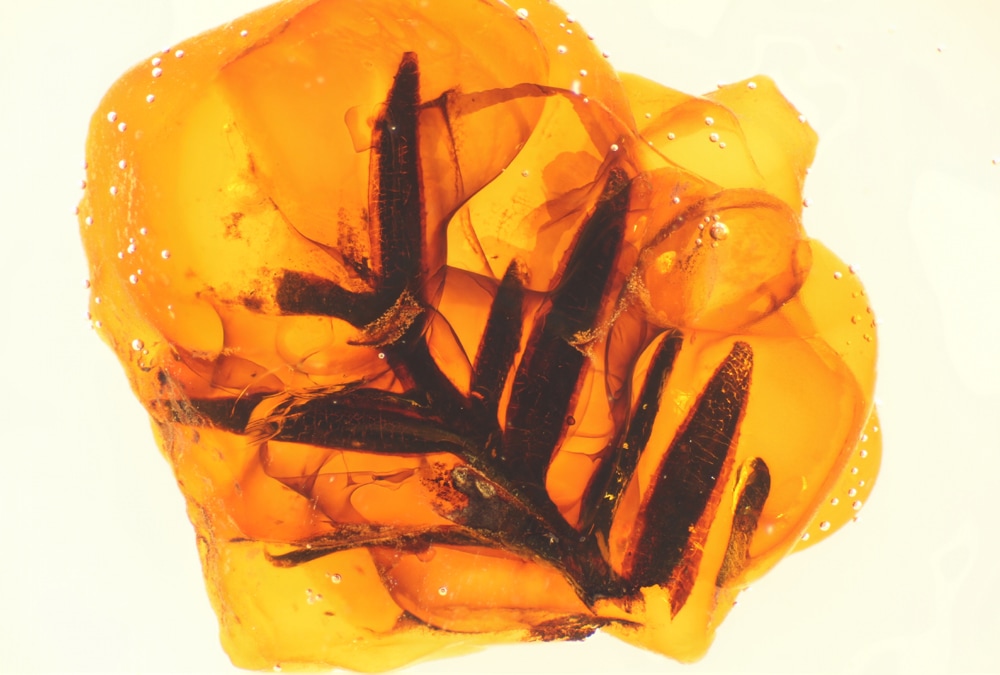
Index fossils (sometimes called guide fossils) are a special category of fossils that only occur in a specific location(s), therefore are often used to identify and define specific geologic periods (or faunal stages). www.virtualmuseumofgeology.com/fossils-gallery.html What is Amber? Amber is fossilized resin of a coniferous tree of early Tertiary. One of the differences between resin and sap is the latter's solubility in water since most of it is water from the xylem (water transporting system) of the tree. In this type of fossilization, the organism is entrapped in a biologically inert environment and preserved as a whole. Intact insects are often found in amber, though they may be altered slightly. Many physical and chemical agents of abiotic environment (the oxidative air and temperature) and biotic factors (bacteria and scavengers) accelerate the decomposition of a dead organism. Avoidance of these factors aids in preserving the organism and in the amber formation. The Process of Amber Formation: Organisms fall or drop into the resin when it first exudes out of the tree. Essential oils, called Oleoresins, compose most of the first deposited resin. This substance is volatile and is often lost through the years. Additional resin then falls on top and gives the organism its typical suspended appearance. The resin then hardens through a process called polymerization and becomes less vulnerable to destruction. This hardened resin, called copal, has a higher chance of being fossilized than pliable resin. As the copal ages, concentration of the essential oil decreases while the copal progressively oxidizes the resin and polymerization continues. The copal slowly turns into amber millions of years after the first entombment of the organism. The only way to differentiate between the two elements would be to put them through many physical and chemical tests such as UV light testing, burning, and various other tests. The most famous examples of amber have come from the Baltic Sea region (Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Denmark, the former Soviet Union, Great Britain, Estonia, Latvia, and Holland). Because of the presence of microscopic air bubbles, Baltic amber tends to appear cloudy or milky. The hue varies with quantity and quality of the bubbles. www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/paleo/fossils/amber.html Getting Into The Fossil Record - Teacher's Guide: www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/explorations/tours/fossil/ http://www.oum.ox.ac.uk/thezone/funstuff/games/pdfs/twist.pdf http://files.havefunteaching.com/free-worksheets/grade/third/science/fossils-worksheet-2.pdf |
Details
Author:
|
|
|
Contact:PHONE: (513) 695 - 1337
EMAIL: [email protected] HOURS: Monday - Friday 7:30am - 4:00pm (except holidays) Connect:Warren County Soil & Water Conservation District Copyright © 2016
Warren SWCD Privacy Notice. Emails are serviced by Constant Contact. Constant Contact's Privacy Notice. |